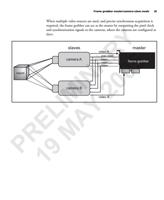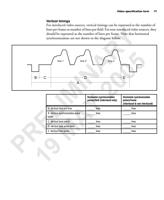
Digital video signals 89
image information increases. For monochrome images, as n increases, more shades
of gray are available, which results in a more accurate representation of the grabbed
image. The following illustrates 8-bit digital data:
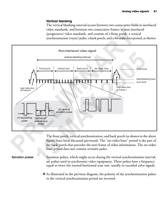
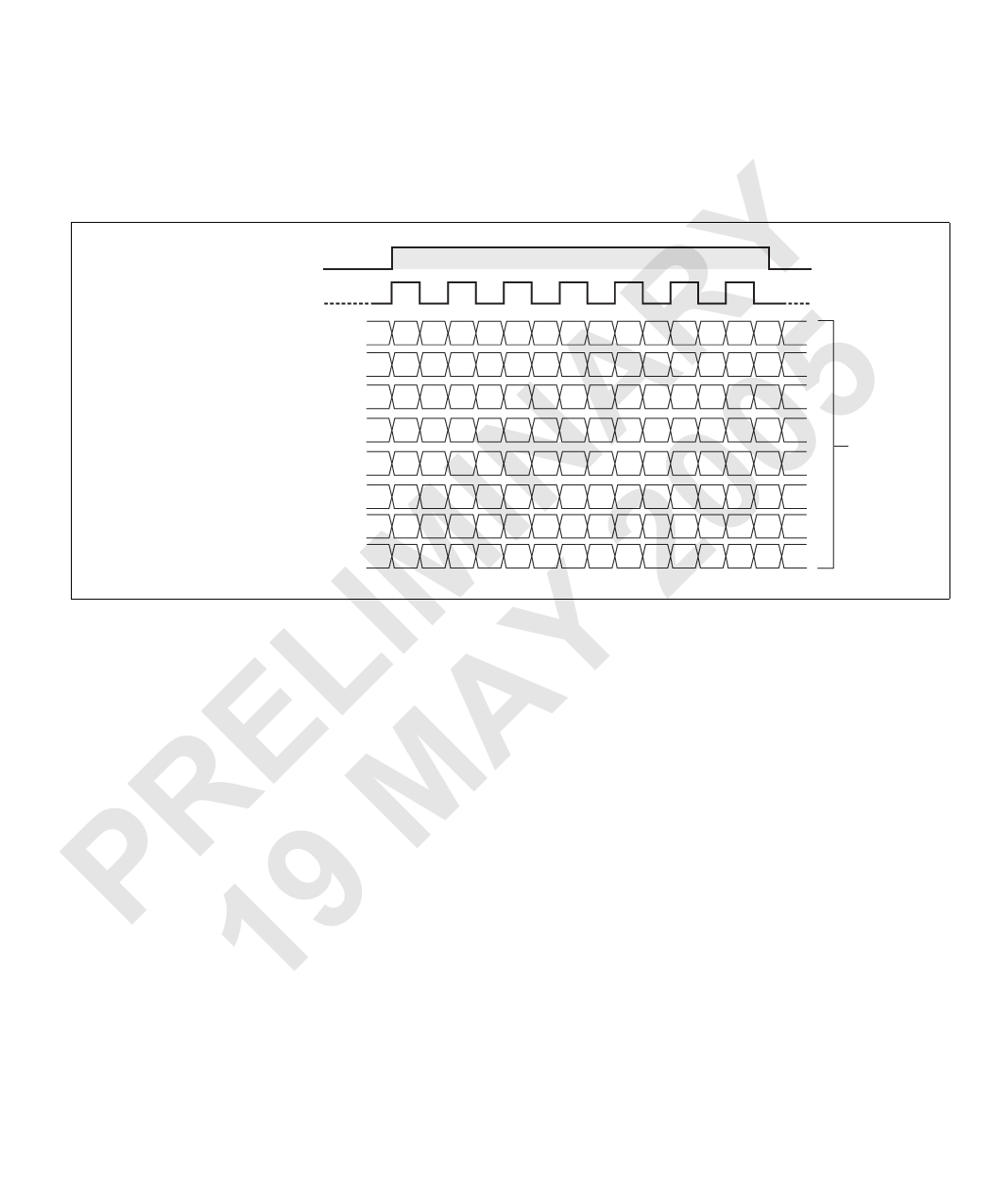
Y Each pixel is defined by the
sampling of a single line at a
certain point in time. In this
8-bit example, the pixel is
R represented with 256
A 5 brightness values (28 = 256).
pixel clock
bit 0
1
bit 1
bit 2
bit 3
bit 4
IN 0 bit5
bit 6
0 bit 7
line valid
n
digital data
IM 2 Digital video data is usually transmitted on a pixel-by-pixel basis in the form of
several bits in parallel. Each bit is transmitted on an individual SIGNAL line, using
the TTL logic levels standard, or on a pair of signal lines, using differential RS-422
L Y or EIA-644 (LVDS) standards. Other digital formats includes Camera Link.
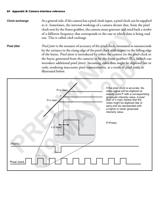
E A RS-422
With RS-422, digital information can travel over a longer distance without the
introduction of as much noise as with TTL. It is a medium-range
differential-signaling pair signal standard.
R M In differential signalling, both positive and negative voltages are used. It
determines binary values based on polarity and not on absolute voltage values.
P 9Therefore a signal can be clearer even with a lot of degradation.
1TTL
TTL (transistor-transistor logic) is a common type of digital circuit. The TTL
format signal is characterized by the voltage levels of 0 Volts representing the
logical 0, and 5 Volts representing the logical 1; however, with noise and longer
transmission distances, the signal can be downgraded so that determining the 0/1
is from the voltage left is erroneous.