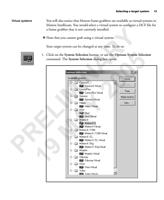
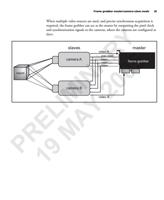
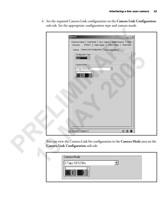
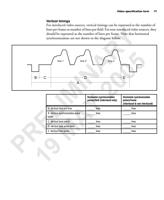
74 Appendix B: Camera interface reference
Interfacing overview
This chapter serves as an introduction to video and interfacing a camera to Matrox
hardware. It will help you understand the descriptions and diagrams in your
camera manual, and allow you to get your system up and running more quickly.
Y Depending on your level of knowledge, certain sections might be more useful to
you than others:
R • Video formats. Identifies the various standard and non-standard video formats.
A 5 • Standard analog video signal. Describes how a standard analog video signal is
produced, and also explains the various components of the video signal. This
IN 0 section also introduces some digitization-specific topics: pixel clock, AC coupling
and DC restoration.
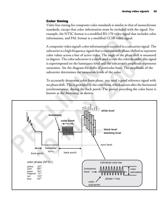
0 • Color timing. Describes basic concepts specific to a color video signal.
IM 2 • Non-standard video formats. Describes some non-standard video formats.
• Camera modes of operation. Discusses the modes of operation for frame scan and
line scan cameras.
L Y Video formats
E A All video signals conform to a particular video format. The video format specifies
such information as the type of video signal (analog or digital), synchronization
R M signals, and number of lines in an image. There are standard and non-standard
video formats.
P Standard video formats
9The RS-330 and RS-343 standards (used in the United States, Canada, and Japan)
1are monochrome video formats based on the RS-170 standard but have additional
signal characteristics by way of modified timing waveforms and more restrictive
tolerances. The CCIR video standard (used in Europe) is also a monochrome video
standard similar to the RS-170 standard except that it lacks a pedestal (black and
blanking levels are equal).