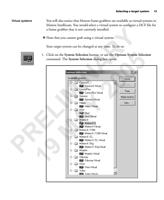
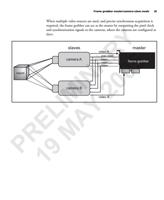
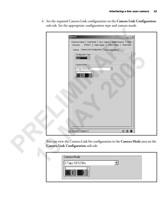
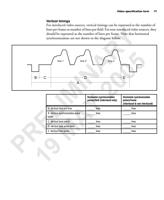
76 Appendix B: Camera interface reference
Non-standard video formats
Non-standard video formats include digital video, high resolution video, and
negative-going video.
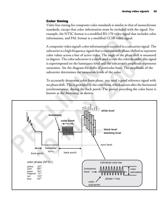
• Digital video is a digitized video waveform, where the synchronization and
intensity (luminance) levels have been assigned a digital value. Digital video can
be of any resolution, from very low to very high.
Y • High resolution video includes any camera with a spatial resolution of 1024 pixels
x 1024 lines and higher. The difference between this type of analog video signal
R and a standard analog video signals is the difference in the timing specifications
and the signal period, along with the increased sampling rates required by the
A 5 frame grabber.
IN 0 • Negative-going video is an analog video signal where white or bright pixel data is
represented by a more negative voltage than black or dark pixel data.
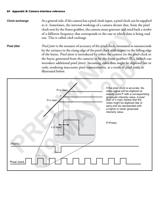
0 Data exchange protocols
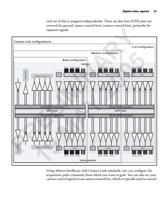
There are several data exchange protocols including LVDS, RS-422 and Camera
IM 2 Link. The data exchange protocol of choice is Camera Link. Camera Link is a
high speed communications interface. You can download a copy of the Camera
Link specifications from the Automated Imaging Association website
L Y (http://www.machinevisiononline.org). Refer to the sub-section Camera Link
standards for further details.
E A Analog video signals
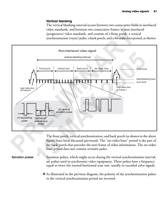
R M How the video signal
P 19 is produced
This section describes how analog video signals are produced, and explains the
various components of the video signal.
A video camera contains a two-dimensional area of photosensors (such as a
charge-coupled device). These photosensors convert the energy of incident light
particles into equivalent electrical charges. The charge of each sensor is then
scanned out of the camera, in a left-to-right, top-to-bottom fashion, producing a
continuous analog video signal that will eventually be digitized.