Page 114 of 120
114 Appendix B: Camera interface reference
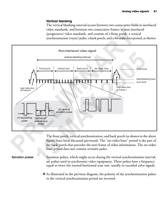
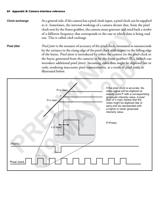
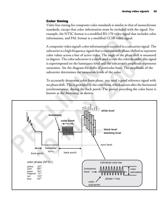
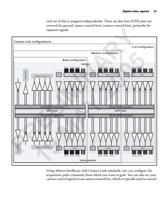
Summary of camera modes
The following tables summarize the various camera modes for frame scan and line
scan cameras. Note that "internal" refers to the camera end and "external" refers
to the frame grabber end.
Y Frame scan cameras
Camera Modes
R Continuous mode:
• Continuous video.
A 5 • Internal exposure control.
Connections
• Video and synchronization signals between
camera and frame grabber (synchronization
signals can be provided by the frame grabber).
• Exposure time cannot exceed frame transfer
IN 0 time.
• Fixed frame rate is independent of exposure time.
0 Pseudo-continuous mode:
• Continuous video.
• Video and synchronization signals between
camera and frame grabber.
IM 2 • Internal exposure control.
• Exposure time can be much longer than frame
transfer time.
L Y • Frame rate is a function of exposure time.
Asynchronous reset mode:
E A • Internal exposure control.
• External trigger.
R M Control mode:
• External exposure control.
P 9• External trigger.
• Video, synchronization, and exposure (frame
grabber acting as asynchronous reset) signals
connected between camera and frame grabber.
• External trigger signal connected to frame
grabber.
• Video, synchronization, and exposure (frame
grabber acting as asynchronous reset in addition
to actual exposure) signals connected between
camera and frame grabber.
• External trigger signal connected to frame
1 grabber.
Long exposure or integration mode:
• Internal or external exposure control.
• Exposure times longer than one frame.
• External trigger.
• Video, synchronization, and exposure (trigger)
signals connected between camera and frame
grabber.
• External trigger signal connected to frame
grabber.