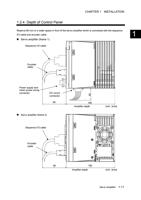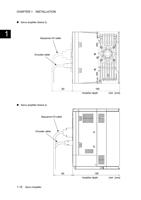
CHAPTER 2 WIRING
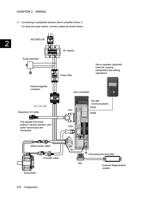
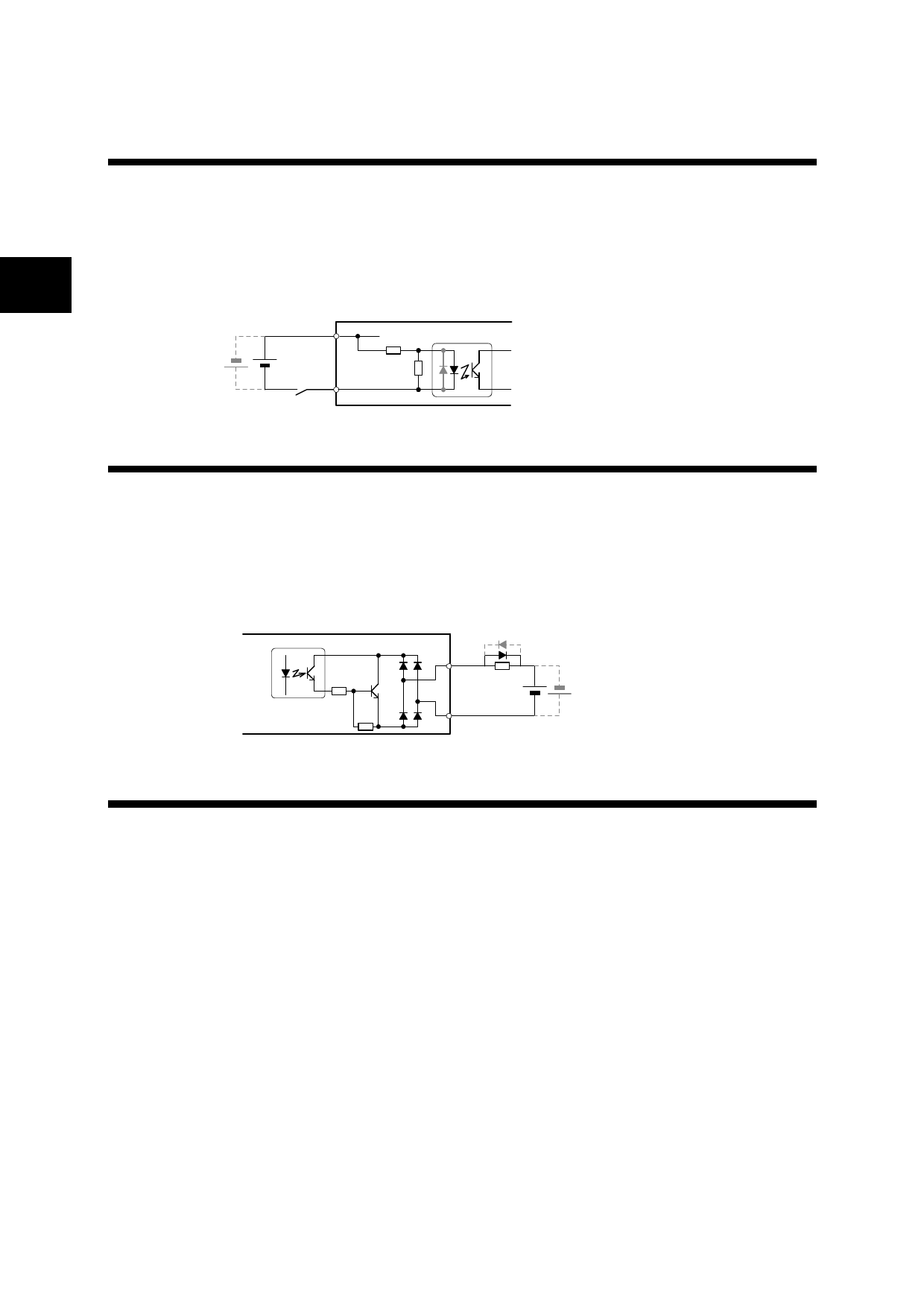
2.1.3.5 Sequence Input (CONT1, CONT2, CONT3, ... COMIN)
This is the input terminal for sequence control.
The terminal allows sink input/source input.
Use the terminal within the range from 12 VDC to 24 VDC.
2
A current of approx. 8 mA (for 24 VDC) is consumed at each point.
The terminal function can be changed by setting the parameter. For assignable signals, refer to
page 2-20.
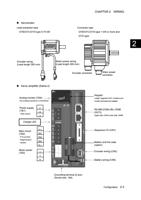
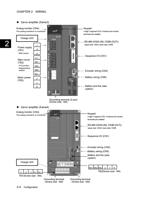
COMIN
1D2Ct1o22~4 V2D4CV
CONTn
13..03kkΩ
1.56k8Ω0
Seサrvoーamボpアlifieンr プ
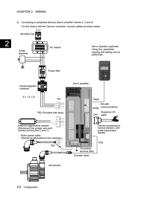
2.1.3.6 Sequence Output (OUT1, OUT2, ... COMOUT)
This is the output terminal for sequence control.
The terminal allows sink output/source output.
Use the terminal within the range from 12 VDC to 24 VDC.
A current of approx. 8 mA (for 24 VDC) is consumed at each point.
The terminal function can be changed by setting the parameter. For assignable signals, refer to
page 2-21.
Sサervーo aボmアplifンierプ
OUTn
DC24VV
COMOUT
2.1.4 RS-485 Communications (CN3)
Use the RS-485 communications by connecting other servo amplifiers, host controller or PC.
Use a marketed straight cable (RJ45) with all wires connected.
There is no need to connect the terminator.
Max. 31 servo amplifiers can be connected.
RS-485 communications can be applied in two communications: Modbus-RTU protocol
communications and PC Loader protocol communications.
Use PA2_97 (communication protocol selection) to select the protocol.
However, select the Modbus-RTU protocol to perform immediate value operation.
For details, refer to “CHAPTER 13 RS-485 COMMUNICATIONS.”
2-14 Configuration