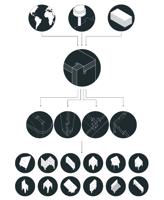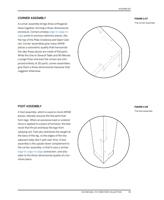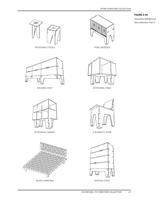
MASSING MODEL AND STOCK MATERIAL
MASSING MODEL AND STOCK
MATERIAL
In the earliest stage of designing, it helps to
start with rough, abstract elements, and then
develop the design by gradually going into
greater and greater detail. In this section, you’ll
make the first move by creating a massing
model—an abstracted solid model of the object
you’re making—in this case, a bench.
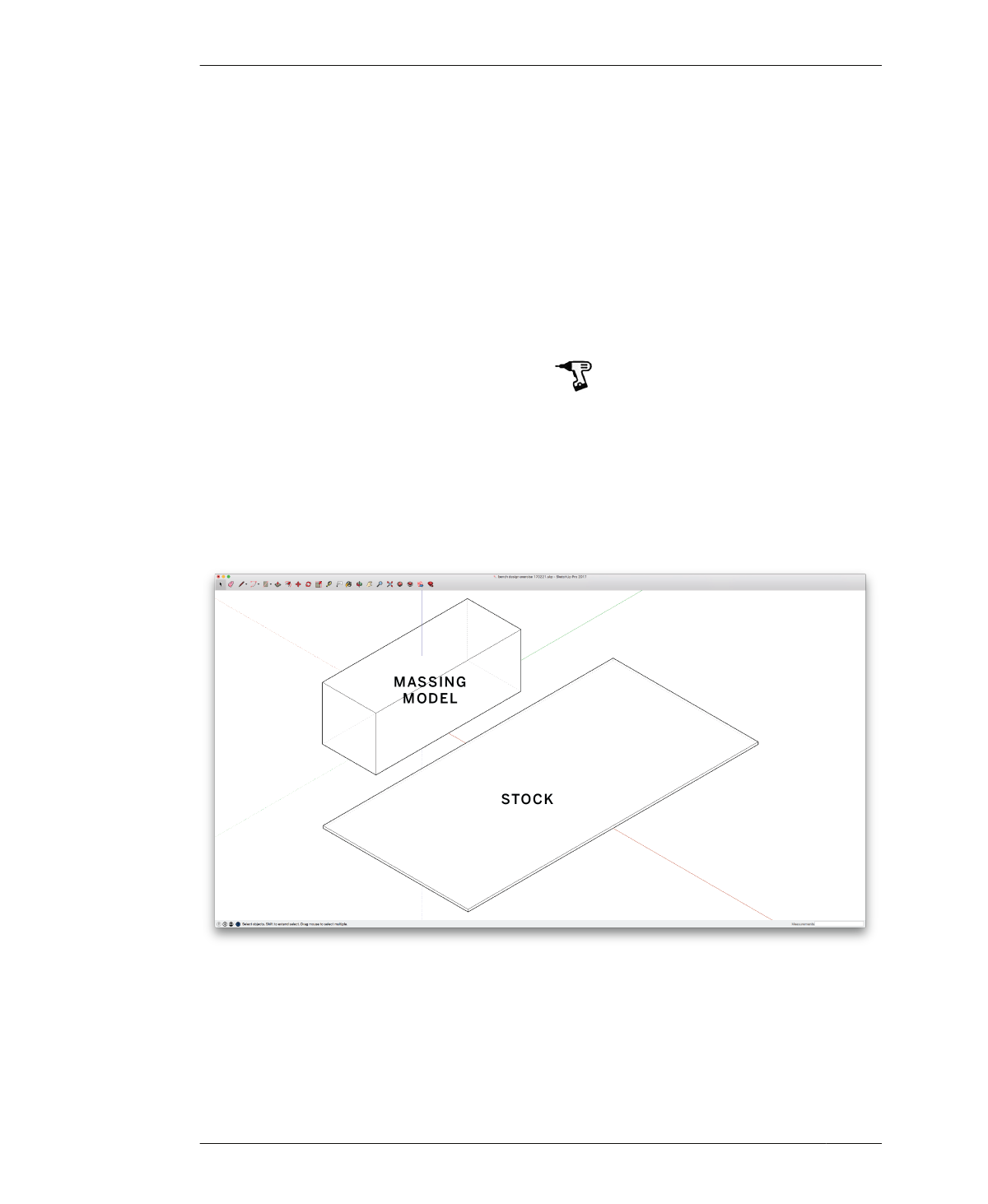
As you first make this rudimentary, three-
dimensional massing block, use your program
research as a starting point. Dimensions
derived from general ergonomic standards for
a two-seater bench are 48″ long by 18″ deep
and 18″ high (1220 mm × 450 mm × 450 mm).
You’ll also model a standard sheet of plywood,
or material stock. You’ll use this stock as the
source for creating every bench part. By model-
ing your bench parts from copies of this stock,
you’ll ensure that each has a consistent mate-
rial thickness.
You’ll use ¾″ as the material thickness of your
stock. This is a standard nominal thickness,
referred to as the variable TNOM, and used
throughout this book. Chapter 5 delves into
TNOM and working with sheet material thick-
ness.
Imperial to Metric Units
For this exercise, a standard sheet of 4′ × 8′
plywood converts to the metric standard,
1220 mm × 2440 mm. The nominal ¾″ mate-
rial thickness converts to 19 mm.
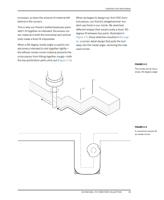
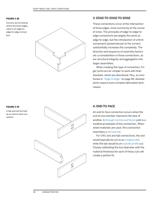
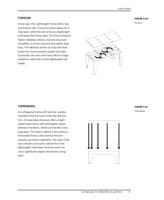
FIGURE 4-3
Material stock along-
side bench massing
92
DESIGN FOR CNC