PROTOTYPING
PROTOTYPING
Prototypes are used to evaluate a design at
varying stages during the design and fabrica-
tion process.
From a practical standpoint, prototyping allows
you to identify errors and troubleshoot defects
before committing to making a full-scale, final
piece. From a design standpoint, prototypes
enable you to take risks with innovative ideas
and to gather immediate feedback. Working
digitally enables rapid prototyping, where you
can iteratively cycle through a process of
designing, prototyping, and making improve-
ments, over and over.
Prototypes can take many forms, but for CNC
furniture there are two kinds that are especially
useful. Partial prototypes made at full scale are
essential to digital craftsmanship, by helping
you to dial in machine settings and to evaluate
finishing techniques. Scale prototypes, made
by fabricating your digital file at a smaller scale,
are great for evaluating a new or modified
design.
PARTIAL PROTOTYPES
Partial prototypes are small samplers of a larger
design that you make using your actual project
material. A partial prototype is great for trying
out especially complex and tricky portions
within the design, before committing to the fab-
rication of an entire design. Partial prototypes
are also quite useful for evaluating joinery fit
and ensuring that you scaled the CAD file to
perfectly match TMAX.
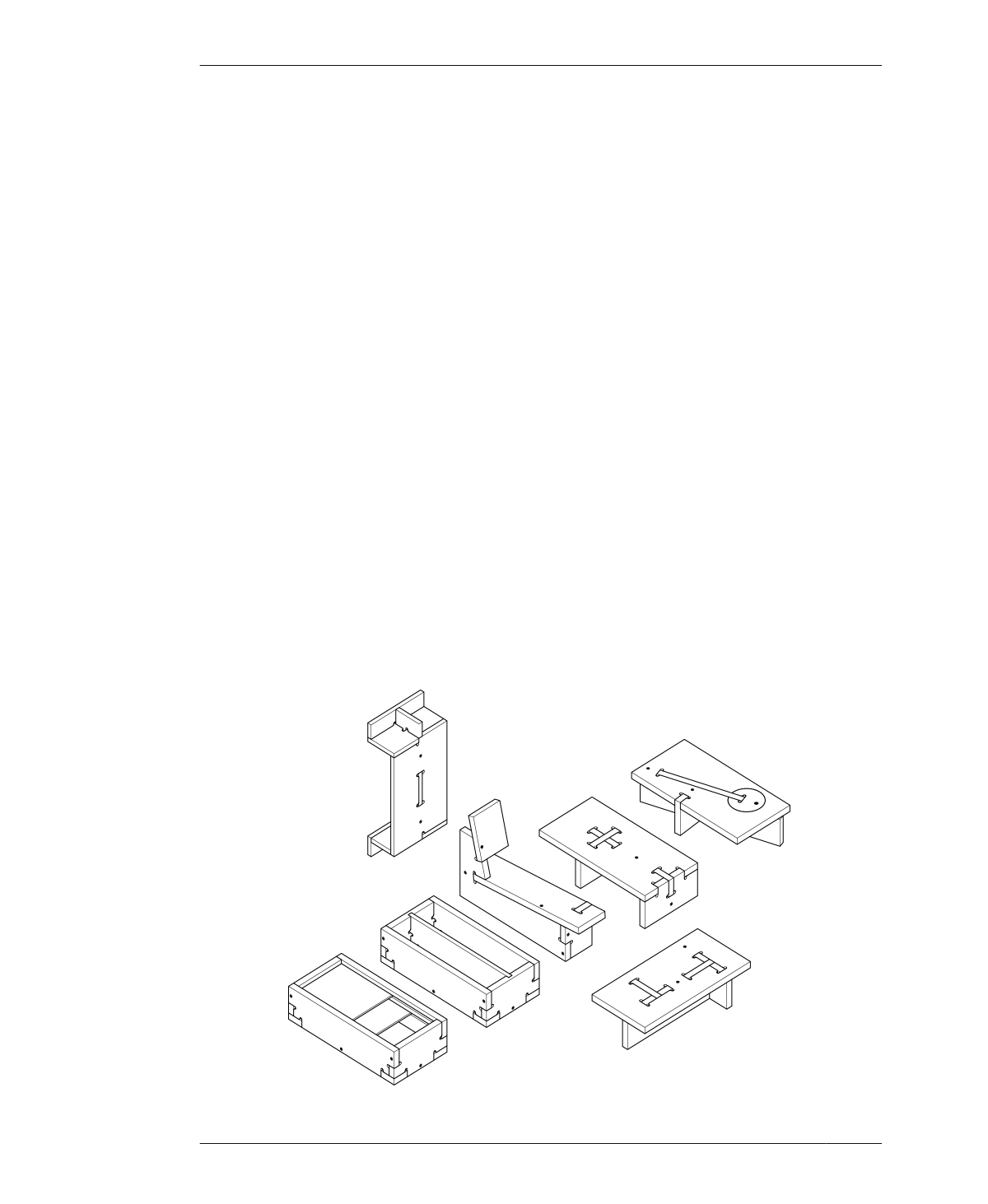
TEST PIECES
Each project in this book is accompanied by a
partial prototype called a test piece, shown in
Figure 5-8 and in the image that opens this
chapter. They were designed to simulate the
most complex joint combinations within each
project. After measuring materials and scaling
a CAD file, fabricating this test piece is the next
step for ensuring tight-fitting joinery.
FIGURE 5-8
Partial prototype test
pieces for each project
136
DESIGN FOR CNC
