Page 52 of 100
Functional Details 45
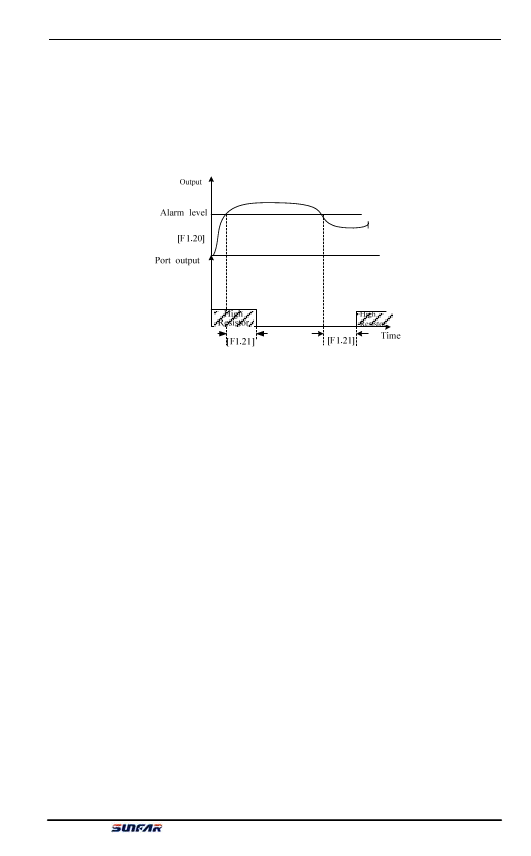
3: Overload detection
When the inverter’s output current exceeds the overload alarm level, after the set
alarm delay time, it outputs effective signals. When the inverter’s output current is
lower than the overload alarm level, after the same delay time, it outputs void
signals.
Figure 6-11 Overload Alarm
4: Frequency reaching upper limit
When the inverter’s output frequency reaches the upper limiting frequency, this
terminal outputs effective signals; otherwise, it outputs void signals.
5: Frequency reaching lower limiting
When the inverter’s output frequency reaches the lower limiting frequency, this
terminal outputs effective signals; otherwise, it outputs void signals.
6: Running at zero speed
When the inverter’s running command is effective and the output frequency is at 0,
this terminal outputs effective signals; otherwise, it outputs void signals.
7: Under voltage stop
When the inverter’s DC side voltage is lower than the specified value, the inverter
stops running, and this terminal outputs effective signals; otherwise, it outputs void
signals.
8: Inverter fault
When the inverter stops running due to fault, it outputs effective signals; and when
the inverter runs normally, it is at void status.
9: Disconnection fault
When the inverter stops running due to disconnection fault, it outputs effective
E550 Series Universal Low-Power Inverter